
Experimental vs Theoretical Probability Theoretical vs Experimental
Experimental versus theoretical probability simulation (video) | Khan Academy AP®︎/College Statistics Course: AP®︎/College Statistics > Unit 7 Lesson 1: Estimating probabilities using simulation Math > AP®︎/College Statistics > Probability > Estimating probabilities using simulation Experimental versus theoretical probability simulation

Seventh grade Lesson Theoretical vs Experimental Probabilities
Courses on Khan Academy are always 100% free. Start practicing—and saving your progress—now: https://www.khanacademy.org/math/cc-seventh-grade-math/cc-7th-p.

PPT Experimental Vs. Theoretical Probability PowerPoint Presentation
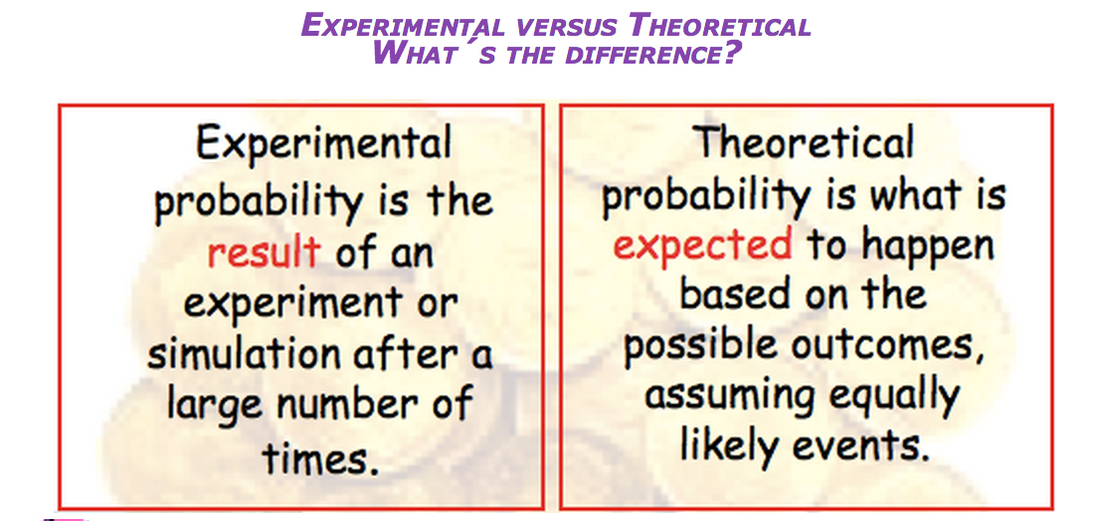
Theoretical probability is what we expect to happen, where experimental probability is what actually happens when we try it out. The probability is still calculated the same way, using the number of possible ways an outcome can occur divided by the total number of outcomes.

Illustrating Experimental Probability and Theoretical Probability YouTube
Blake S 6 years ago Experimental probability is the results of an experiment, let's say for the sake of an example marbles in a bag. Experimental probability would be drawing marbles out of the bag and recording the results. Theoretical probability is calculating the probability of it happening, not actually going out and experimenting.
Unit 6 Probability
Figure 4-4 shows a graph of experimental probabilities as n gets larger and larger. The dashed yellow line is the theoretical probability of rolling a four of 1/6 \(\neq\) 0.1667. Note the x-axis is in a log scale. Note that the more times you roll the die, the closer the experimental probability gets to the theoretical probability. Figure 4-4

PPT Experimental Probability Vs. Theoretical Probability PowerPoint
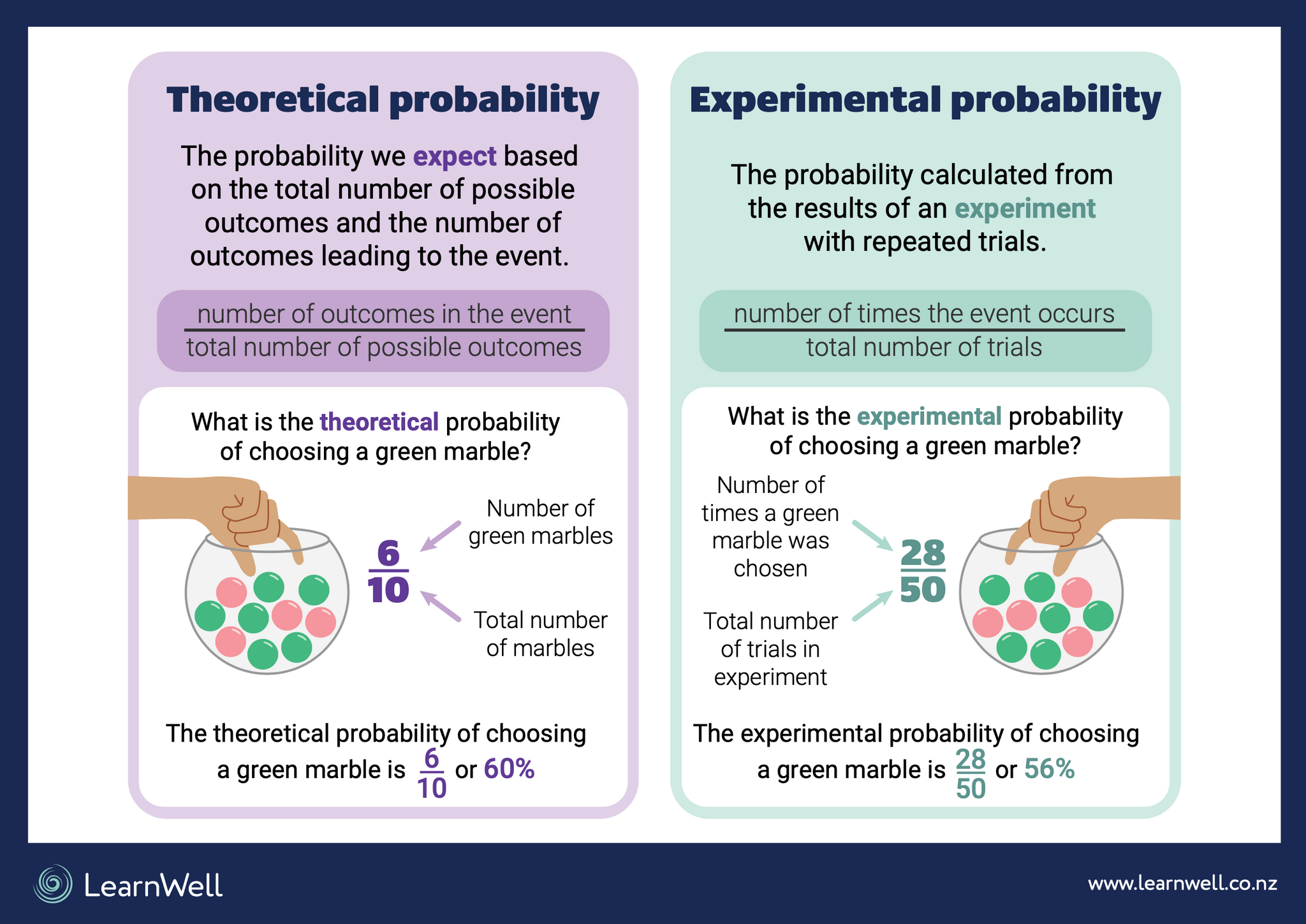
Theoretical probability is calculated by taking the number of favorable outcomes over the total number of outcomes. It can be left as a ratio/fraction, or converted to a decimal. What is the.
Theoretical and Experimental Probability Poster LearnWell
In contrast, Experimental Probability is derived from the number of times an event occurs over the number of trials conducted. Sawaira Riaz. Nov 27, 2023. 8. In Theoretical Probability, calculations are made by assuming each outcome in an experiment is equally likely. Experimental Probability, on the other hand, uses actual data from performing.

PPT Experimental Probability Vs. Theoretical Probability PowerPoint
Experimental Probability Theoretical Probability Prediction Solved Examples Frequently Asked Questions What is Probability? The chance of a happening is named as the probability of the event happening. It tells us how likely an occasion is going to happen; it doesn't tell us what's happening.

Theoretical vs. Experimental Probability YouTube
Choose 1 answer: The experimental probability got closer to the theoretical probability after more flips. A The experimental probability got closer to the theoretical probability after more flips. The experimental probability got farther away from the theoretical probability after more flips. B

PPT Experimental Probability Vs. Theoretical Probability PowerPoint
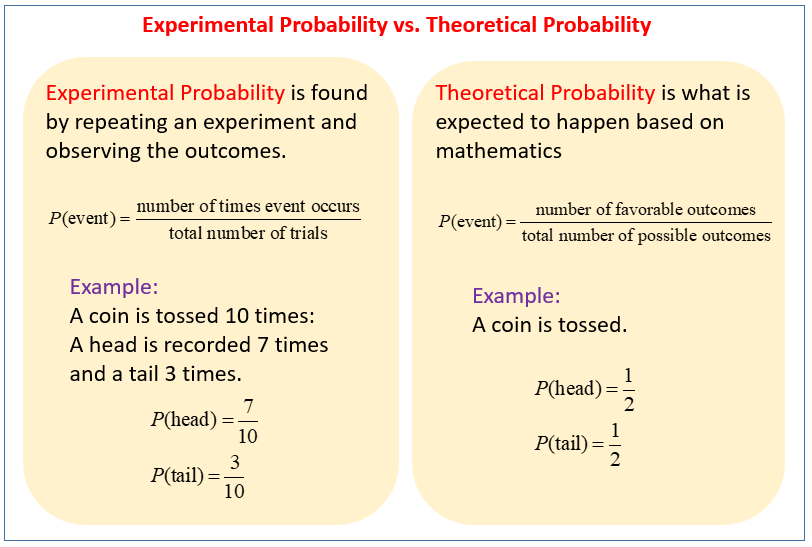
Experimental probability is the ratio of the number of times an event occurs to the total number of trials. In other words, theoretical probability is a ratio that describes what should happen, but experimental probability is a ratio that describes what actually happened. You can use theoretical and experimental probabilities to distinguish.

Theoretical vs Experimental Probability YouTube
The probability that is determined on the basis of the results of an experiment is known as experimental probability. This is also known as empirical probability. What is Experimental Probability? Experimental probability is a probability that is determined on the basis of a series of experiments.

Theoretical vs. Experimental Probability Anchor Chart Poster Anchor
The experimental probability will gradually get closer to the value of the theoretical probability. In this case, the experimental probability will get closer to 25% as the coins is tossed over more times. If you're looking for more experimental vs.theoretical probability examples, feel free to try out this question. It'll require you to do.

PPT Experimental vs. Theoretical Probability PowerPoint Presentation
Comparing Theoretical And Experimental Probability. The following video gives an example of theoretical and experimental probability. Example: According to theoretical probability, how many times can we expect to land on each color in a spinner, if we take 16 spins? Conduct the experiment to get the experimental probability.

Theoretical vs. Experimental Probability YouTube
Experimental Probability In this video, we are going to learn about the differences between theoretical and experimental probability. After you finish this lesson, view all of our Algebra 1 lessons and practice problems. Let's use rolling a dice as an example. Use P to represent probability.
Theoretical Probability and Experimental Probability (solutions
Theoretical probability is the likelihood of a certain outcome occurring. So, in short, how likely something is to happen? Imagine, for a moment, that you are going to flip a coin. There are only two possible outcomes to flipping the coin, which is that it lands on either heads or tails.

PPT 11.2 Theoretical and Experimental Probability PowerPoint
Theoretical probability is calculated using mathematical formulas, while experimental probability is based on results from experiments or surveys. In order words, theoretical probability represents how likely an event is to happen. On the other hand, experimental probability illustrates how frequently an event occurs in an experiment.